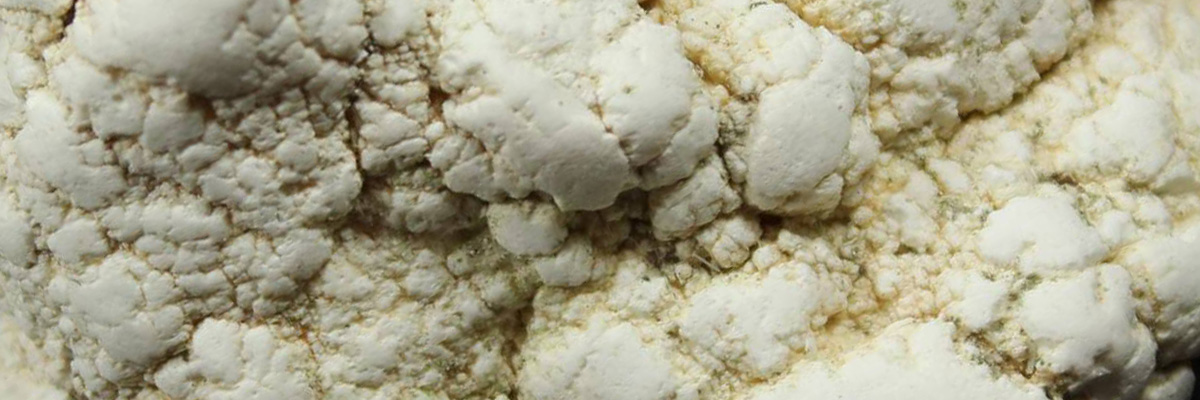
Magnesite is a carbonate mineral that belongs to the calcite group. It is composed primarily of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) and is known for its distinctive, often white or grayish-white color. Magnesite can also occur in shades of yellow, brown, or even pale green, depending on the presence of impurities. It exhibits a vitreous to dull luster and has a porous, earthy texture, which makes it easily distinguishable from other carbonate minerals.
Mineral Makeup
The mineral makeup of magnesite consists predominantly of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), with small amounts of other elements, such as iron, manganese, and calcium. These impurities can alter the color of the mineral, resulting in various shades ranging from white to brown or pale green.
Origin
Magnesite forms through the alteration of magnesium-rich rocks, such as peridotite and serpentinite, during contact with carbon dioxide-rich fluids. This process, known as metasomatism, can occur in a variety of geological environments, including hydrothermal veins and contact metamorphic zones around igneous intrusions.
Occurrence
Magnesite is found worldwide, with significant deposits in Austria, Brazil, China, Greece, Russia, Slovakia, and the United States. It often occurs in association with other magnesium-rich minerals, such as serpentine, talc, and brucite. Magnesite is an important source of magnesium and is used in various industrial applications, including the production of refractory materials, fertilizers, and magnesium metal.
Metaphysical
Magnesite is believed to possess metaphysical properties that promote relaxation, emotional balance, and self-awareness. It is said to help individuals let go of negative emotions, such as anger and resentment, and encourage a more positive outlook on life. Magnesite is also associated with enhanced visualization and intuition, making it a popular choice for meditation and spiritual practices.
| Class | Sedimentary (Chemical) |
| Mineral Makeup | Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), with possible impurities of iron, manganese, and calcium |
| Luster | Vitreous to dull |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 3.5-4.5 |
| Streak | White |
| Color | White, grayish-white, yellow, brown, or pale green |
| Cleavage | Perfect rhombohedral |
| Specific Gravity | 2.9-3.1 |