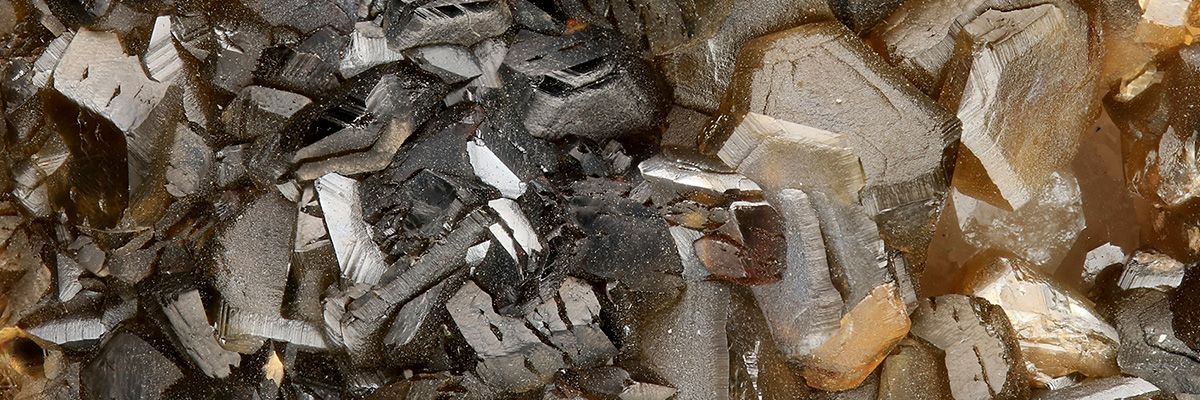
Siderite is an iron carbonate mineral belonging to the trigonal crystal system, characterized by its yellowish to brownish color, and a vitreous to pearly luster. The mineral typically forms rhombohedral, scalenohedral, or prismatic crystals, though it may also occur in massive or granular aggregates. Siderite is a common component of sedimentary iron deposits and can be found in various geological environments, often in association with other iron-bearing minerals.
Usage
Siderite has been historically used as an iron ore, though it is now considered a less significant source of iron compared to hematite and magnetite. The mineral has also been used as a pigment in ceramics and as a component in the production of steel. In addition, siderite is valued by mineral collectors for its crystal habits and association with other interesting minerals.
Gemstone
Siderite is not typically considered a gemstone due to its relatively low hardness and muted color palette. However, well-formed crystals and specimens displaying unique crystal habits can be appreciated by mineral collectors and enthusiasts for their aesthetic qualities.
Origin
Siderite forms in various geological environments, including sedimentary, hydrothermal, and metamorphic settings. The mineral is commonly formed through the precipitation of iron-rich fluids in low-temperature, oxygen-poor environments such as bogs, swamps, and marine sediments. Siderite can also form as a result of hydrothermal alteration or metamorphism of iron-bearing minerals, as well as through biogenic processes involving iron-reducing bacteria.
Occurrence
Siderite can be found worldwide, with notable deposits occurring in Europe, North America, and Australia. In the United States, siderite is commonly found in the Appalachian region, the Great Lakes area, and the Rocky Mountains. In Europe, significant siderite occurrences are found in Austria, Germany, and the Czech Republic. These regions are known for their rich geological history and diverse mineralogy, making them important sources of siderite for scientific study and collection.
Metaphysical
In metaphysical and spiritual practices, siderite is believed to possess grounding and stabilizing properties. The mineral is said to help individuals connect with the earth’s energies, promoting a sense of balance and stability. Siderite is also considered a stone of transformation, assisting with personal growth and the release of negative emotions. Additionally, the mineral is believed to enhance one’s intuition, creativity, and manifestation abilities.
| Class | Carbonates |
| Formula | FeCO3 |
| Luster | Vitreous to pearly |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 3.5 – 4.5 |
| Streak | White |
| Color | Yellowish to brownish, sometimes gray or greenish |
| Cleavage | Perfect in three directions, forming rhombohedra |
| Specific Gravity | 3.7 – 3.9 |