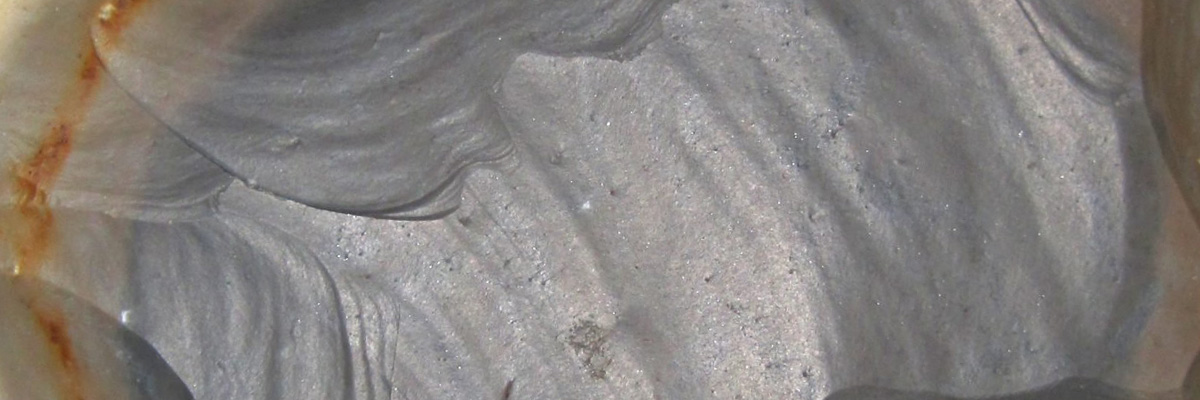
Chert is a fine-grained sedimentary rock that belongs to the chemical and biochemical subclass. It is characterized by its microcrystalline texture, hardness, and conchoidal fracture, making it an ideal material for creating sharp-edged tools. Chert comes in various colors, such as red, brown, black, and green, depending on its impurities and the environment in which it formed.
Mineral Makeup
The primary mineral component of chert is microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz (also known as chalcedony), which gives the rock its distinctive hardness and durability. Chert may also contain trace amounts of other minerals, such as calcite, dolomite, or various types of clay minerals, depending on its formation process.
Origin
Chert forms through the accumulation and compaction of silica-rich sediments, primarily derived from the remains of microscopic organisms such as diatoms and radiolarians. In some cases, chert can also form through the replacement of calcium carbonate in limestone, a process known as silicification. Over time, pressure and chemical processes transform these silica-rich sediments into the dense, fine-grained rock known as chert.
Occurrence
Chert is found in various geological settings around the world, often occurring in limestone and dolomite formations or as nodules within shale and clay deposits. Geographically, chert can be found in the Flint Hills of Kansas, the English chalk cliffs, and the Franciscan Formation in California, among other locations.
Metaphysical
Chert is thought to possess metaphysical properties that promote balance, resilience, and stability. It is believed to help individuals adapt to change and maintain a sense of emotional equilibrium during times of upheaval. Chert is also said to enhance mental clarity, concentration, and focus, making it a valuable stone for those seeking to improve their decision-making abilities.
| Class | Sedimentary (Chemical) |
| Mineral Makeup | Primarily microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz (chalcedony), with possible trace amounts of calcite, dolomite, or clay minerals |
| Luster | Waxy to dull |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.5-7 |
| Streak | White or colorless |
| Color | Red, brown, black, or green, depending on impurities and formation environment |
| Cleavage | None, exhibits conchoidal fracture |
| Specific Gravity | 2.6 to 2.7 |