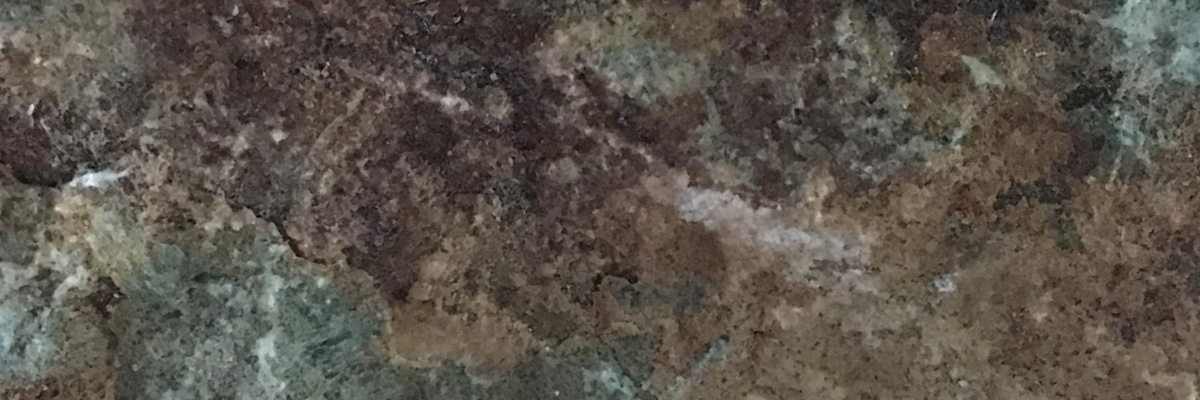
Chlorite is a group of phyllosilicate minerals characterized by their sheet-like structures and green color. These minerals belong to the chlorite group within the larger silicate class. Chlorite exhibits a range of physical characteristics, including a green to black color, a vitreous to pearly luster, and perfect cleavage in one direction. The mineral can form as fine-grained aggregates or well-formed, platy crystals that can be translucent to opaque.
Usage
Chlorite minerals have various applications, primarily in the industrial sector. Due to their heat resistance and chemical stability, they are used as a filler material in the manufacturing of ceramics, paints, and plastics. Additionally, chlorite is utilized in the oil and gas industry as a component of drilling muds, which help lubricate and cool drilling equipment. In the environmental sector, chlorite is used for the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants from water, soil, and air.
Gemstone
While chlorite is not typically considered a gemstone due to its softness and perfect cleavage, it can be found as inclusions within other gemstones, such as quartz, where it creates unique and visually appealing patterns. These gemstones, often referred to as “chlorite-included quartz,” are sought after by collectors and can be used for ornamental purposes or as unique pieces of jewelry.
Origin
Chlorite minerals are formed through various geological processes, such as the alteration of other silicate minerals during metamorphism and hydrothermal activity. Chlorite can also form as a secondary mineral in igneous rocks, as a result of chemical reactions between cooling magma and surrounding rock.
Occurrence
Chlorite minerals can be found in a variety of geological environments, including metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary rocks. They are commonly associated with other minerals, such as quartz, feldspar, and mica. Chlorite can be found in several regions around the world, with significant deposits in the United States, Canada, Brazil, Switzerland, and Austria.
Metaphysical
In metaphysical and spiritual practices, chlorite is believed to have cleansing and purifying properties. It is said to help with the release of negative energies and the removal of emotional blockages, promoting balance, harmony, and emotional healing. Chlorite is also associated with the grounding of spiritual energies, helping to connect individuals to the Earth and enhancing their ability to manifest their intentions.
| Class | Phyllosilicates |
| Formula | (Mg,Fe)3(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2·(Mg,Fe)3(OH)6 |
| Luster | Vitreous to pearly |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 2 – 2.5 |
| Streak | White to greenish |
| Color | Green to black |
| Cleavage | Perfect in one direction |
| Specific Gravity | 2.6 – 3.3 |