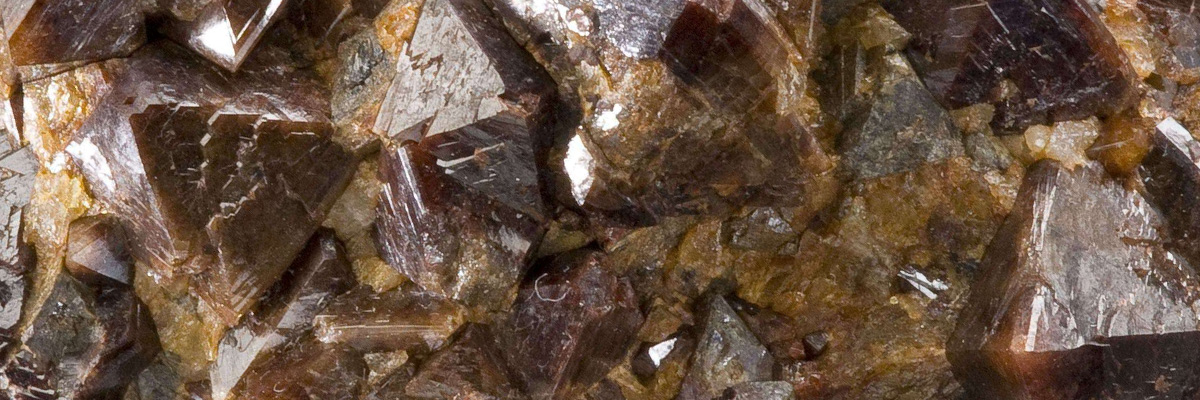
Nesosilicates, also known as orthosilicates, are a group of silicate minerals that consist of isolated silica tetrahedra (SiO4) linked to various metal cations. These minerals play a significant role in the Earth’s crust and are found in a wide range of geological settings, such as igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Nesosilicates are known for their unique crystal structure and diverse range of physical properties, as well as their importance in various industrial applications.
Formation
Nesosilicate minerals primarily form through the cooling and solidification of magma and lava, as well as through metamorphic processes where rocks undergo changes in mineralogy, texture, and composition due to heat, pressure, and the introduction of new chemical elements. They can also form as the end product of weathering processes, precipitating from aqueous solutions to create sedimentary rocks.
Types
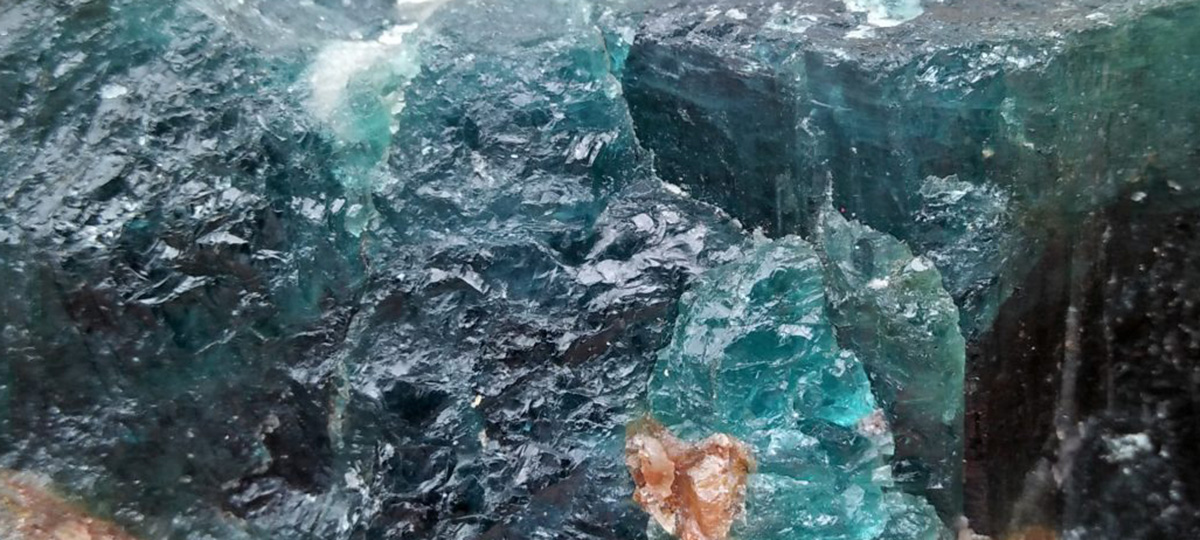
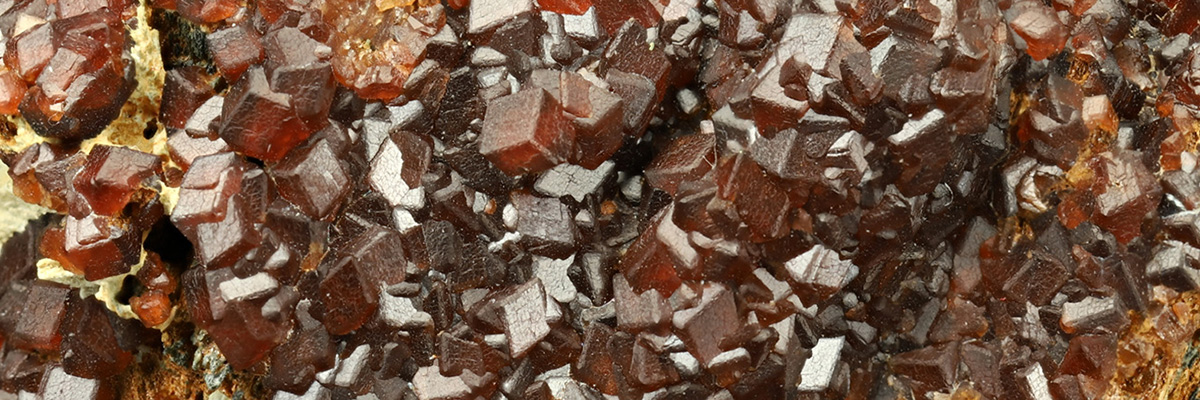
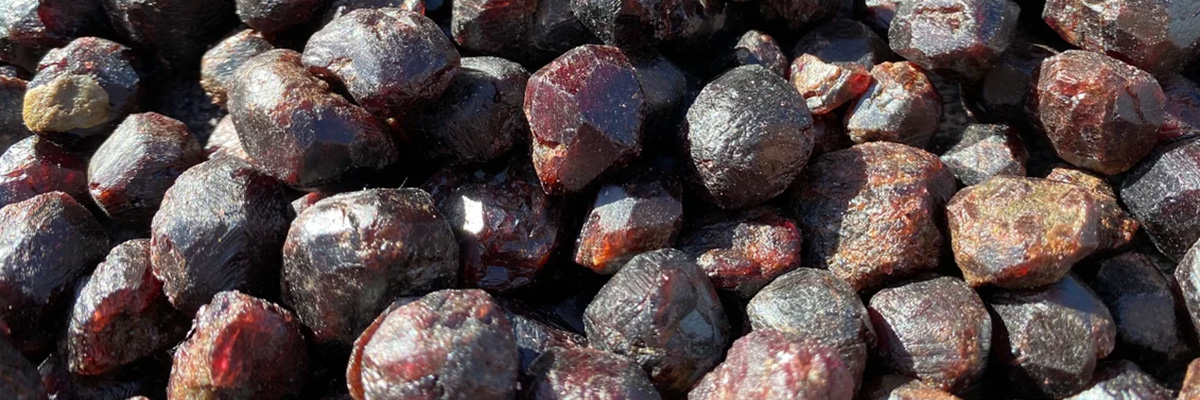
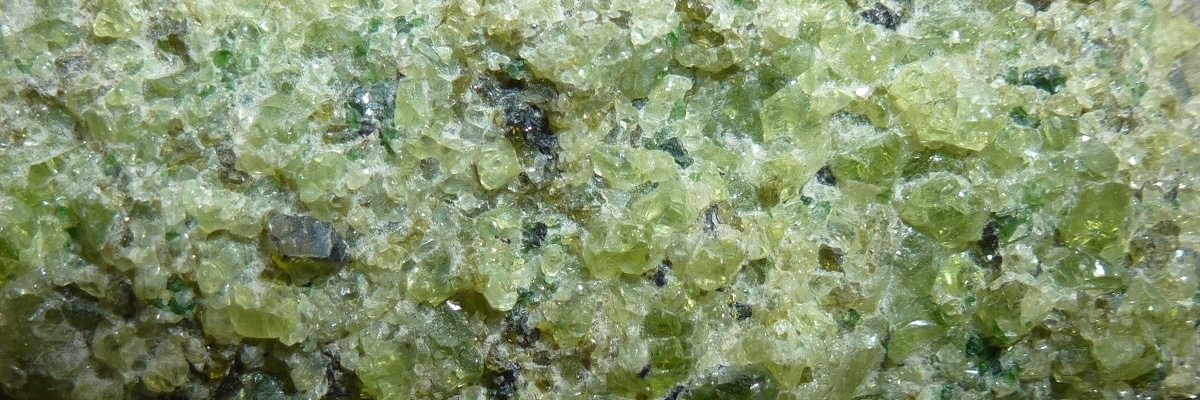
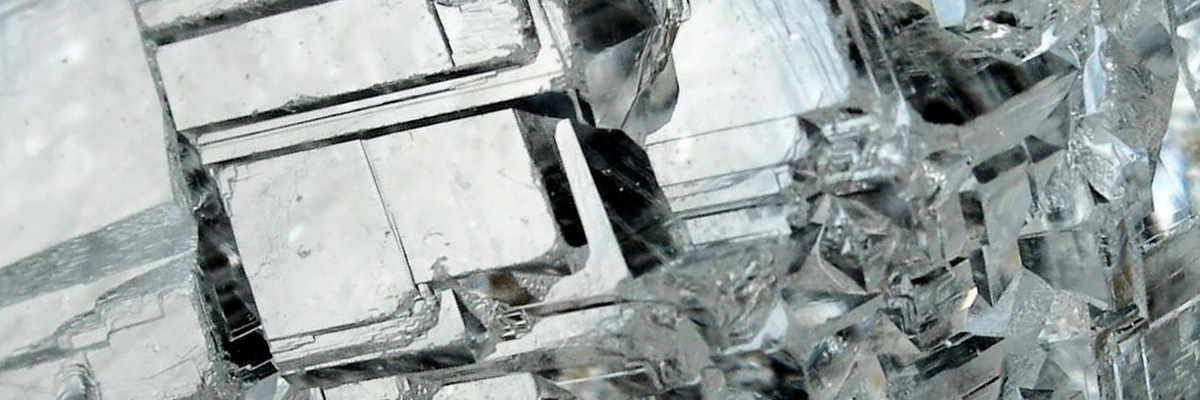
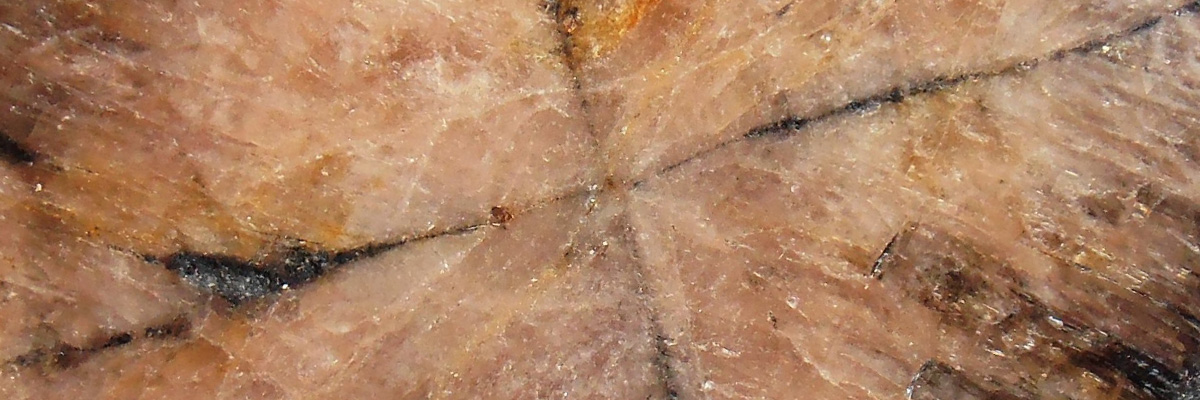
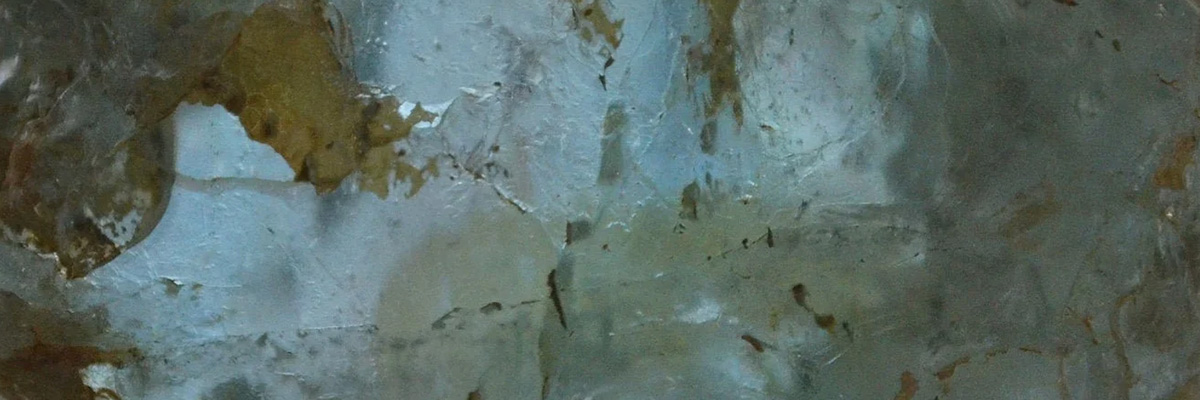
The nesosilicate group contains several notable minerals, including olivine, garnet, and zircon.
- Olivine:
A group of magnesium-iron silicate minerals, olivine is found in igneous rocks, such as basalt and peridotite, and metamorphic rocks like serpentinite. It is the primary component of the Earth’s upper mantle. - Garnet:
A group of silicate minerals with various metal cations, garnets are found in metamorphic, igneous, and some sedimentary rocks. They have a characteristic dodecahedral crystal habit and are often used as abrasives and gemstones. - Zircon:
A zirconium silicate mineral, zircon is found in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. It is known for its excellent resistance to heat and radiation and is often used as a dating tool for ancient rocks, as well as in various industrial applications.
Properties
Nesosilicate minerals exhibit a wide range of physical properties due to their diverse structures and compositions. Their Mohs hardness typically ranges from 3.5 to 7.5, and they can appear transparent, translucent, or opaque. Nesosilicates display various colors and can exhibit different crystal habits, such as dodecahedral, prismatic, or tabular.
Significance
Nesosilicate minerals hold significant importance in various fields. In geology, they provide valuable insights into the geological history of an area, the processes that have occurred, and the formation and evolution of the Earth’s crust.
Nesosilicates also have essential commercial and industrial uses. Olivine is used as a refractory material in the steel industry, as well as in the production of magnesium and as a soil conditioner. Garnets are used as abrasives, waterjet cutting materials, and gemstones, while zircon is employed in the ceramics industry, electronics, and as a gemstone.
Understanding the distribution, properties, and behavior of nesosilicate minerals is crucial for managing natural resources, evaluating geological hazards, and mitigating the environmental impacts of their extraction and use.
Examples
-
Andradite
Andradite is a calcium iron silicate mineral belonging to the garnet group, specifically the nesosilicates class. It is known for its diverse color range, which …
-
Datolite
Datolite is a calcium boron hydroxide silicate mineral belonging to the sorosilicates class, recognized for its diverse color palette that ranges from colorless to white, …
-
Garnet
Garnet is a group of silicate minerals belonging to the cubic crystal system and is part of the nesosilicate subclass. Garnets are known for their …
-
Olivine
Olivine is a magnesium iron silicate mineral belonging to the orthorhombic crystal system and is part of the nesosilicate subclass. This mineral is known for …
-
Phenakite
Phenakite is a beryllium silicate mineral belonging to the cyclosilicates class, known for its transparent to translucent appearance and vitreous to adamantine luster. The physical …
-
Staurolite
Staurolite is an iron aluminum silicate hydroxide mineral belonging to the nesosilicates class, recognized for its distinctive brownish-black to dark brown color and vitreous to …
-
Topaz
Topaz is an aluminum silicate fluoride hydroxide mineral belonging to the orthosilicates class, celebrated for its remarkable range of colors and glassy, vitreous luster. The …
-
Zircon
Zircon is a zirconium silicate mineral that belongs to the nesosilicates class, known for its tetragonal crystal system and striking variety of colors. The general …
Related Posts
-

Metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks are a fascinating class of rocks that have undergone transformation due to intense heat, pressure, or mineral exchange deep within the Earth’s crust. …
-

Organic Sedimentary
Organic sedimentary rocks are unique formations derived from the accumulation and preservation of plant and animal remains, providing a window into Earth’s biological history. These …
-

Chemical Sedimentary
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed from the precipitation of dissolved minerals from water, often due to changing environmental conditions. These captivating rocks offer valuable insights …










