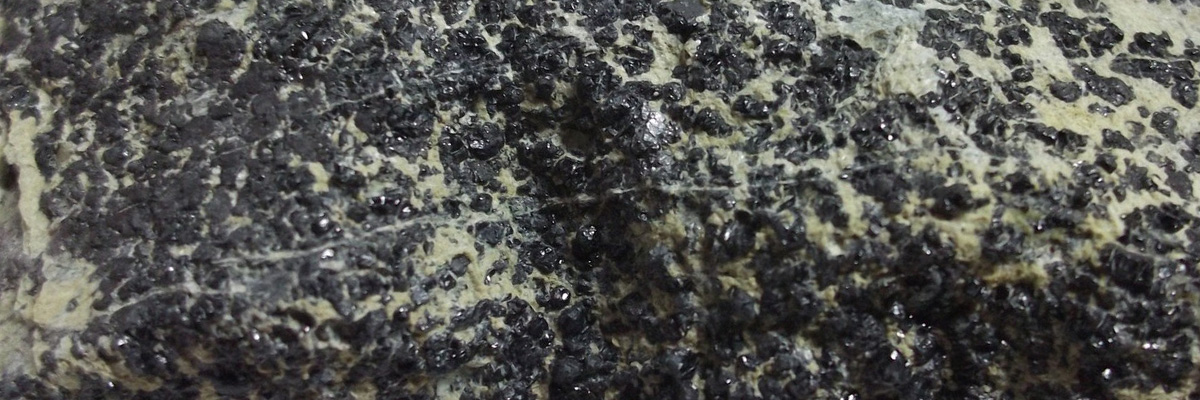
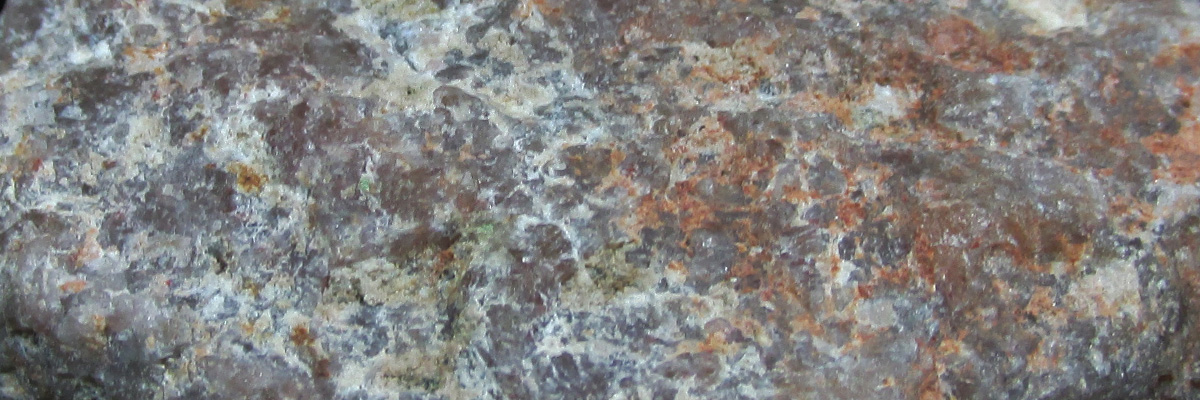
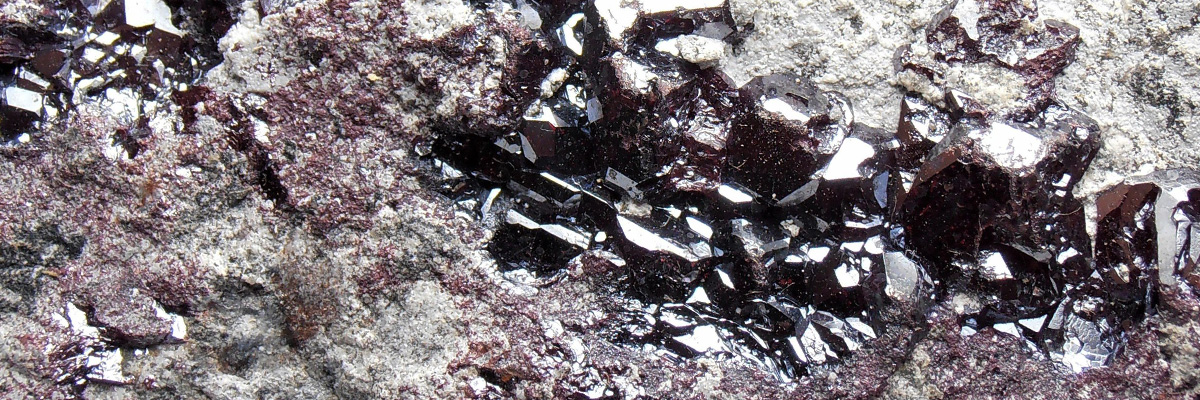
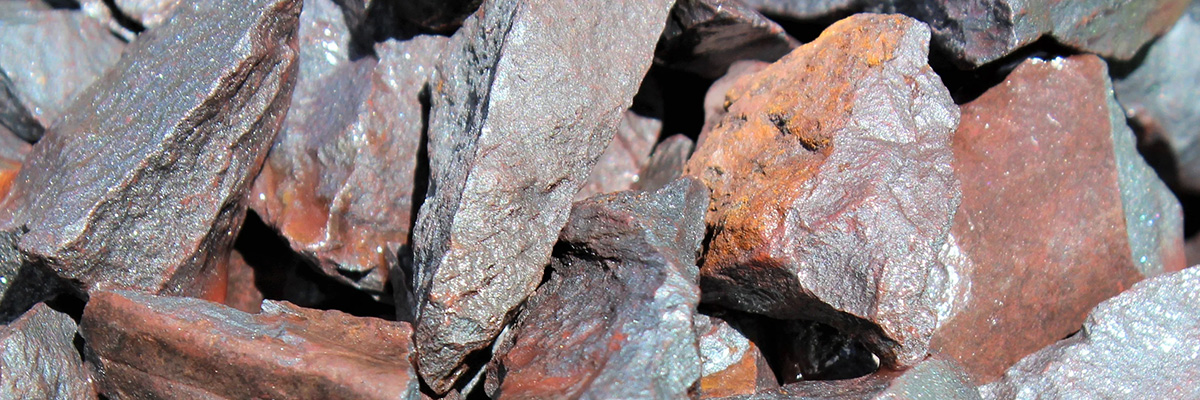
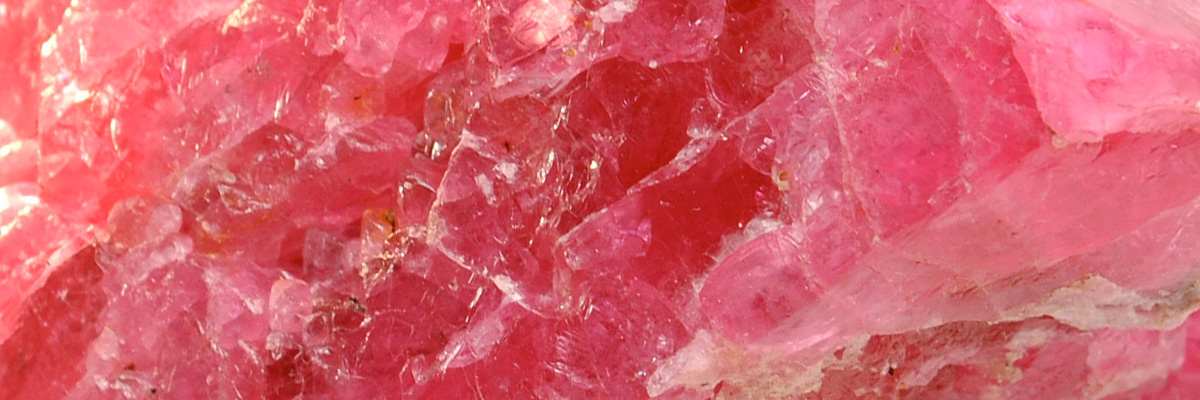
Oxide minerals represent a diverse and essential group of minerals composed of oxygen anions (O2-) combined with metal cations. They can be found in various geological settings, including igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Oxides play a crucial role in the Earth’s crust and are often used as ores for metals, pigments, and other industrial applications.
Formation
Oxide minerals form in diverse geological environments, including high-temperature magmatic processes, metamorphic reactions, weathering of pre-existing minerals, and sedimentary processes. These minerals are formed when metal cations bond with oxygen anions under specific temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions. Oxide minerals are stable under a wide range of geological conditions, making them ubiquitous in the Earth’s crust.
Types
The oxide mineral group includes a wide range of minerals, some of which are:
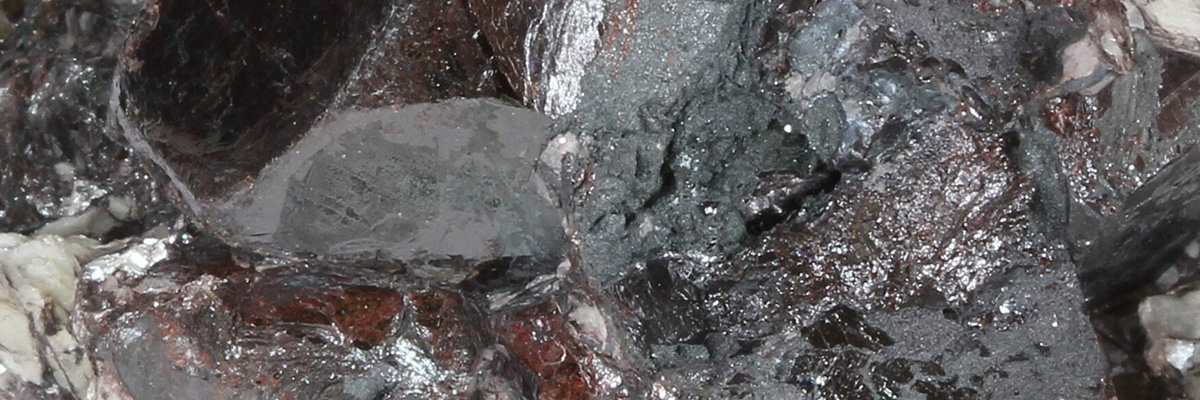
- Hematite (iron oxide):
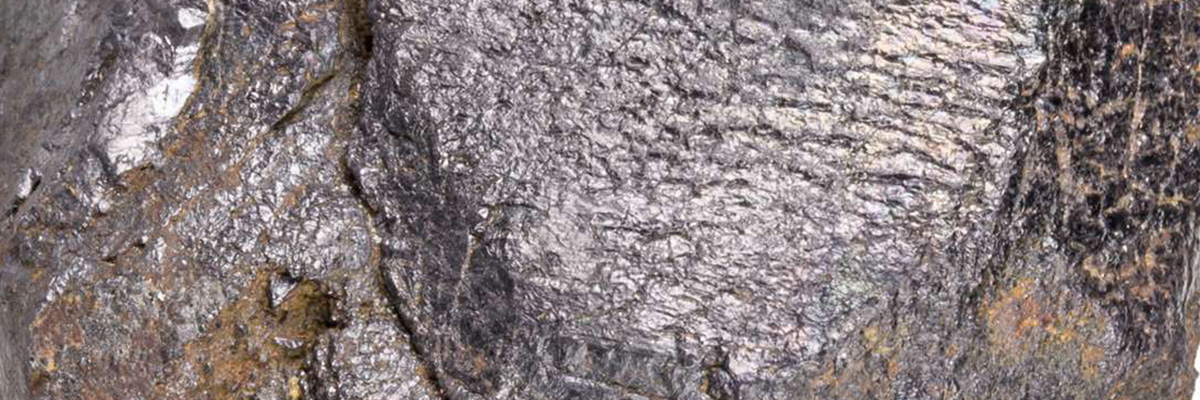
A reddish-brown to silver-gray metallic mineral, hematite is an essential iron ore and the most abundant oxide mineral in the Earth’s crust. It is commonly found in banded iron formations and weathered zones. - Magnetite (iron oxide):
Magnetite is a black, metallic, and magnetic mineral commonly found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. It is also an important iron ore and is frequently used in the production of steel. - Corundum (aluminum oxide):
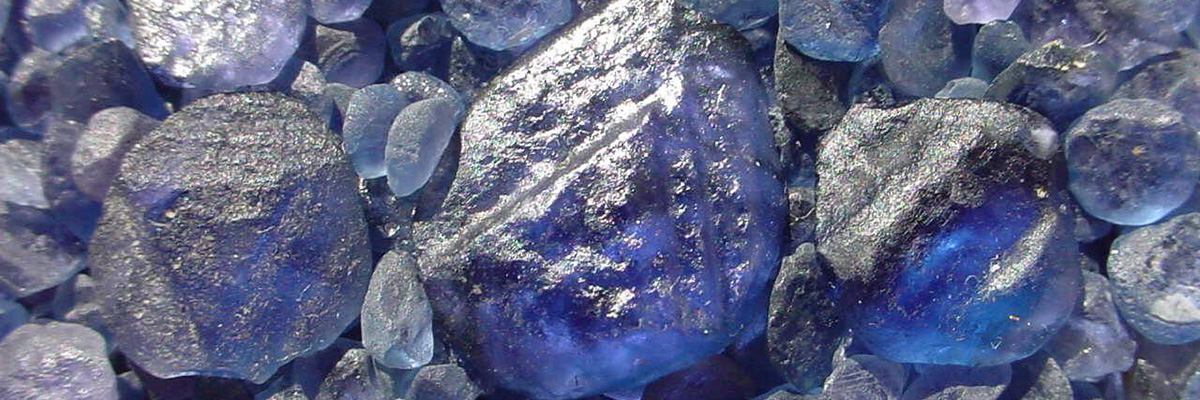
Known for its hardness (9 on the Mohs scale), corundum occurs in various colors, including blue, red, and pink. The gem-quality forms of corundum are sapphire (blue) and ruby (red). - Rutile (titanium oxide):
A reddish-brown to black mineral, rutile is the most abundant source of titanium. It is often used as a pigment in paints, plastics, and paper, and as a source for titanium metal production. - Cuprite (copper oxide):
A red to brown mineral with a high copper content, cuprite is an important source of copper. It is often found in oxidized zones of copper sulfide deposits.
Properties
Oxide minerals exhibit diverse physical and chemical properties depending on their chemical composition and crystal structure. Most oxides are characterized by high densities and hardness. They can be opaque, translucent, or transparent, and their colors range from metallic to various shades of red, brown, black, blue, and green.
Oxides generally exhibit high melting points and are chemically stable in a range of conditions. They can be identified by their characteristic crystal structures, which can be cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, or hexagonal, among others.
Significance
Oxide minerals play vital roles in various fields. In geology, they can provide valuable information about the Earth’s crust’s composition, structure, and geological history. For example, the presence of hematite can indicate the occurrence of banded iron formations, which provide insights into the Earth’s early atmosphere and evolution.
Oxide minerals are also crucial for the extraction of metals and other industrial applications. Hematite and magnetite are important sources of iron for steel production, while corundum’s hardness makes it valuable for abrasives and gemstones. Rutile is used as a pigment and a source of titanium, while cuprite is a primary source of copper.
The study of oxide minerals has environmental significance as well. These minerals can help identify areas with high levels of pollution and can provide insights into the environmental impact of mining and other industrial activities.
Examples
-
Chromite
Chromite is an iron chromium oxide mineral known for its dark brown to black color and metallic to submetallic luster. The mineral’s physical characteristics include …
-
Corundum
Corundum is an aluminum oxide mineral known for its exceptional hardness and durability. Belonging to the oxide class and the hematite sub-class, corundum forms in …
-
Cuprite
Cuprite is a copper oxide mineral known for its striking deep red to reddish-brown color and submetallic to adamantine luster. Belonging to the oxide class, …
-
Hematite
Hematite is an iron oxide mineral known for its characteristic reddish-brown to black color and metallic to earthy luster. Its physical characteristics include tabular, botryoidal, …
-
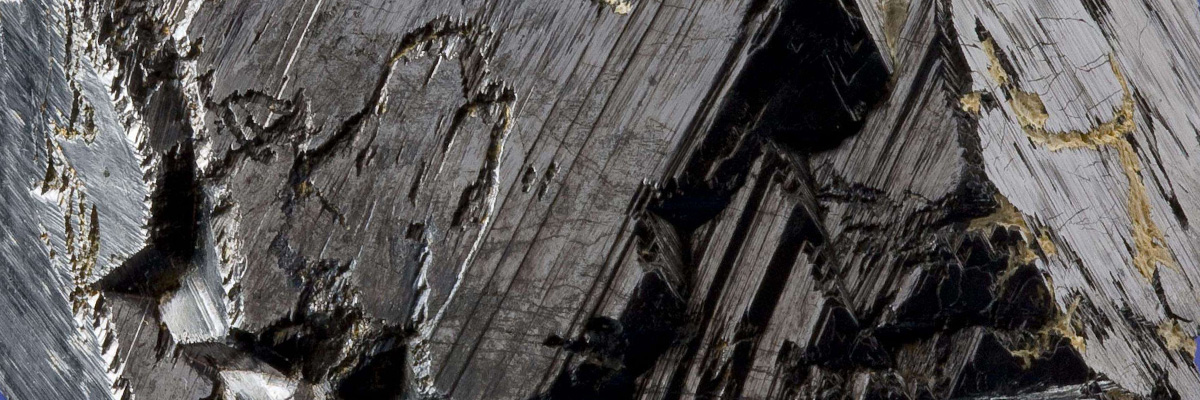
Ilmenite
Ilmenite is an iron titanium oxide mineral known for its black or dark brown color and metallic to submetallic luster. Its physical characteristics include well-formed …
-
Magnetite
Magnetite is an iron oxide mineral known for its strong natural magnetism, metallic luster, and black to brownish-black color. Belonging to the oxide class and …
-
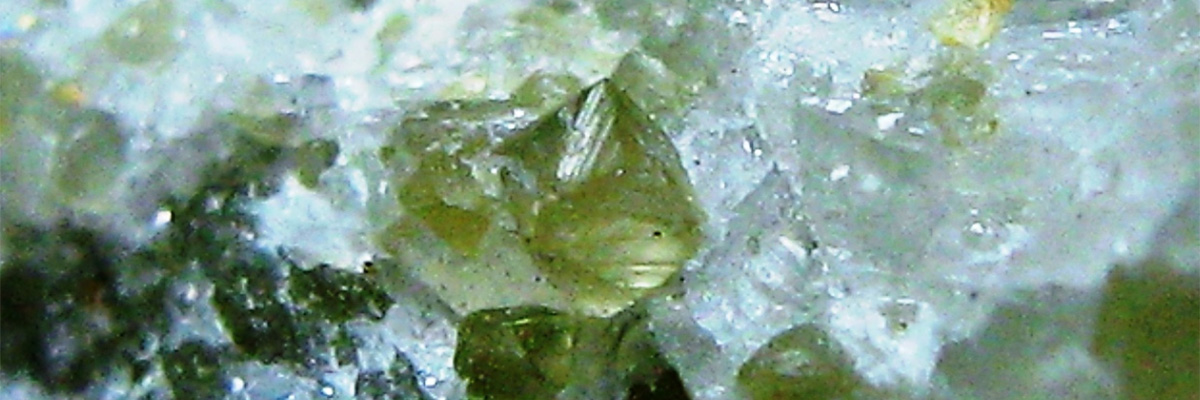
Periclase
Periclase is a magnesium oxide mineral known for its transparent to translucent appearance and vitreous to adamantine luster. Its physical characteristics include a well-formed cubic …
-
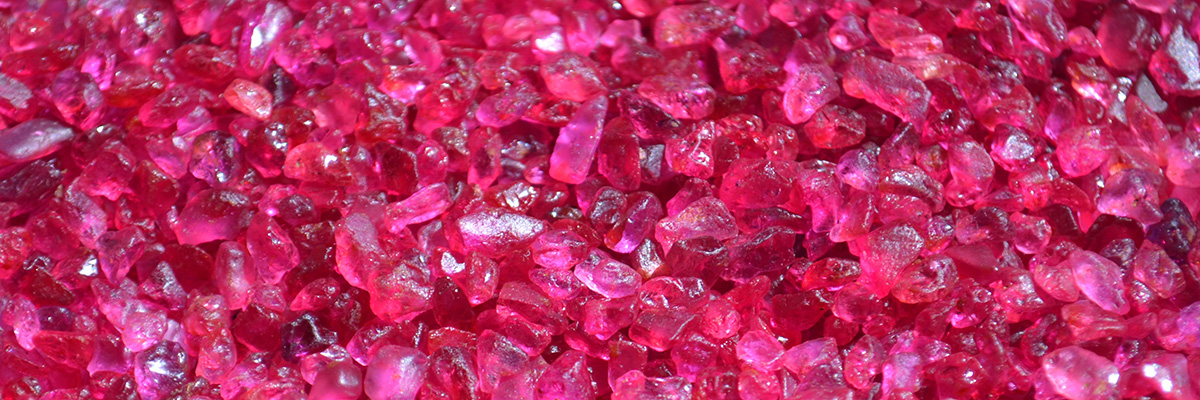
Ruby
Ruby is a red variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminum oxide known for its exceptional hardness and durability. Belonging to the oxide class and …
-
Rutile
Rutile is a titanium dioxide mineral known for its reddish-brown to black color and brilliant adamantine to submetallic luster. Its physical characteristics include well-formed prismatic …
-
Sapphire
Sapphire, a captivating and highly sought-after variety of corundum, is an aluminum oxide mineral belonging to the hexagonal crystal system. This gemstone is best known …
-
Spinel
Spinel is a magnesium aluminum oxide mineral, belonging to the cubic crystal system, and known for its wide variety of vibrant colors, including red, pink, …
Related Posts
-

Mineral Basics
Minerals, naturally occurring substances formed through geological processes, are the essential components of rocks. These substances often take thousands or even millions of years to …
-

Mineral Identification
Mineral identification is the process of determining the name and characteristics of a mineral specimen by using a variety of tests. It is an important …
-

Mohs Hardness Scale
The Mohs Hardness Scale is a universally recognized tool used to classify the hardness of minerals based on their ability to scratch one another. Developed …
-

Native Elements
Native element minerals are a unique and captivating group of minerals composed of a single chemical element in their pure form. They can be found …