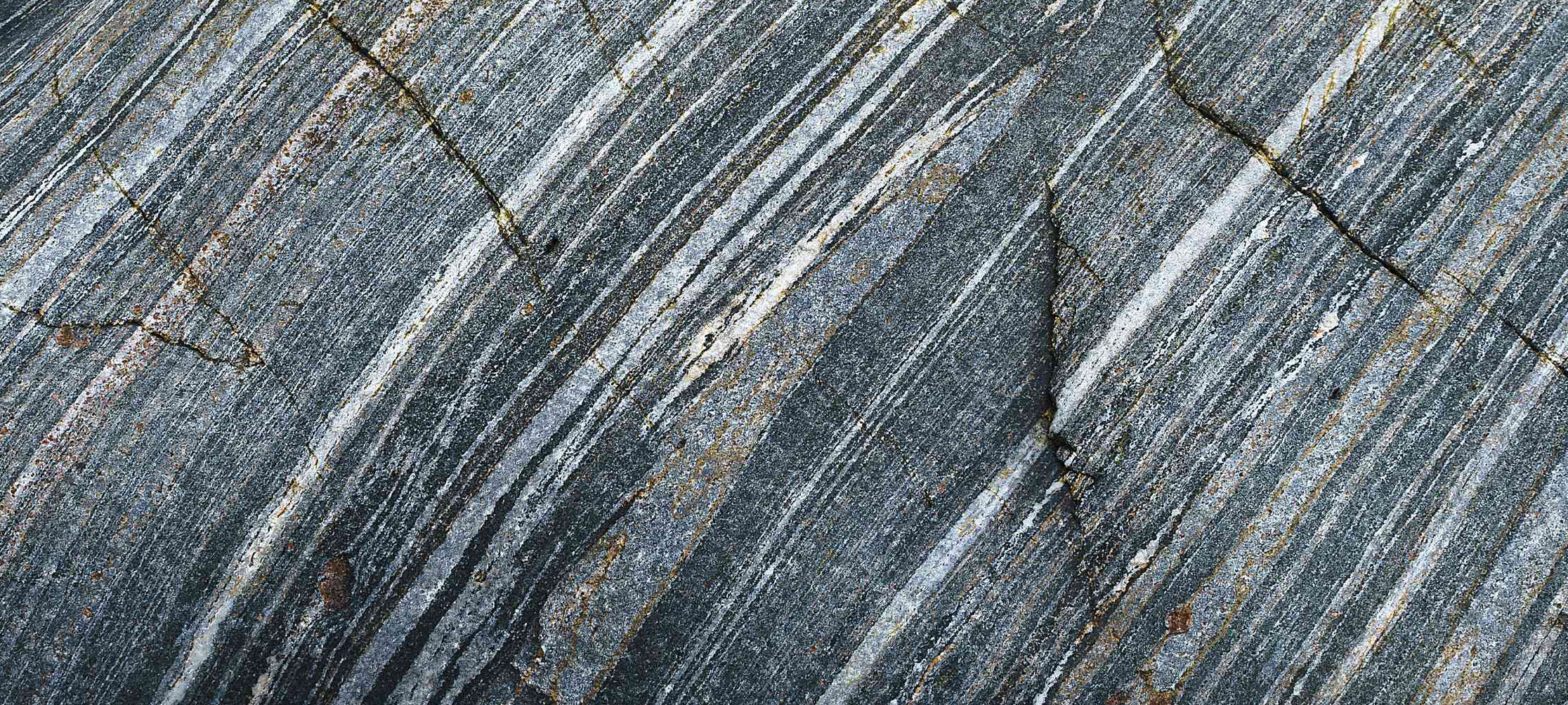
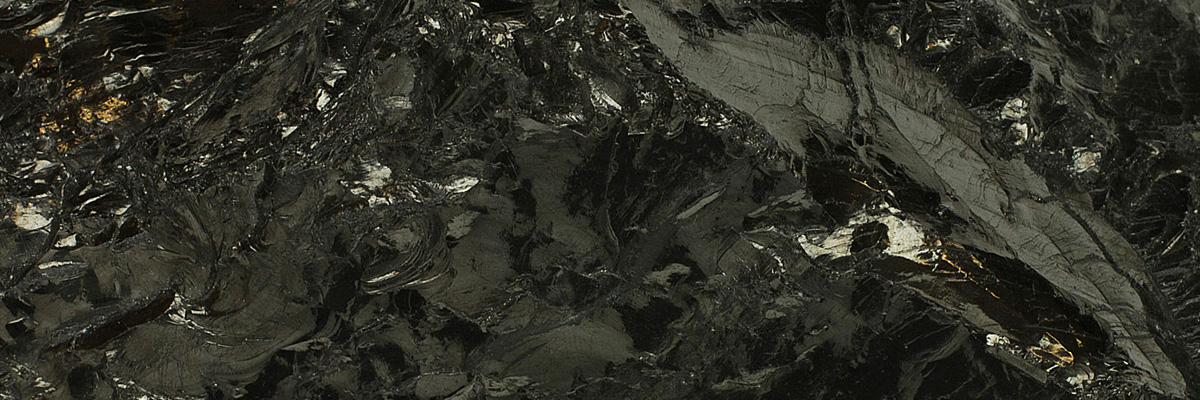
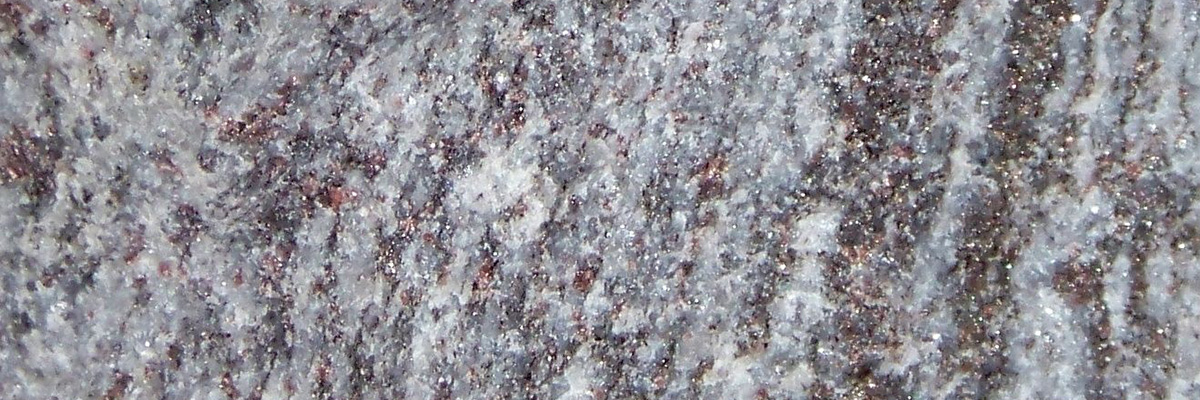
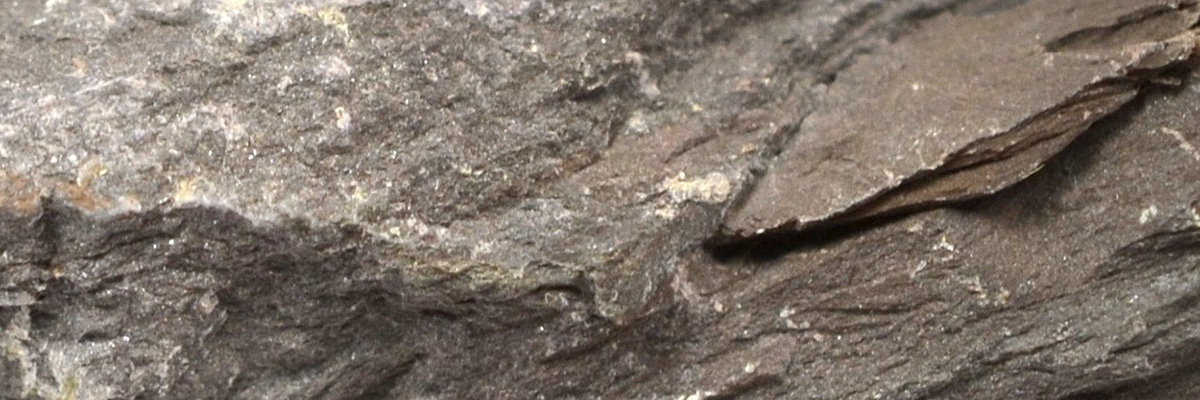
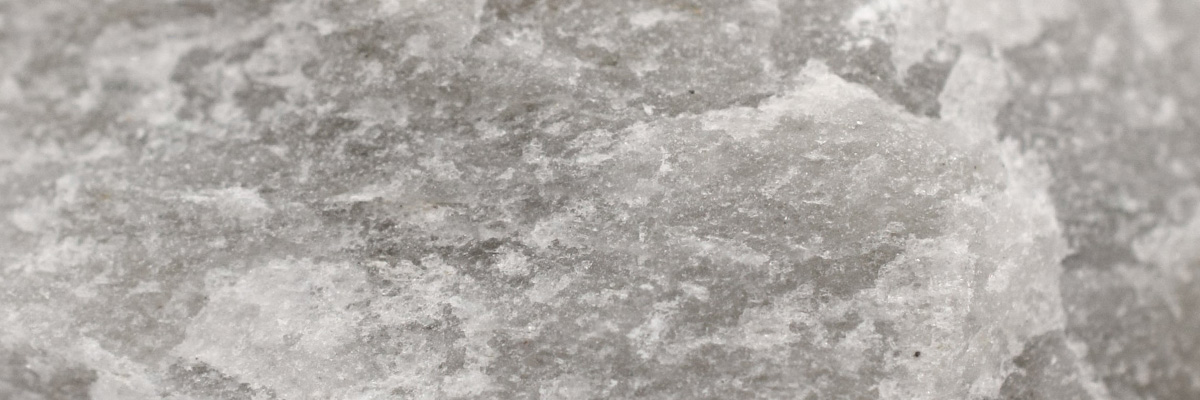
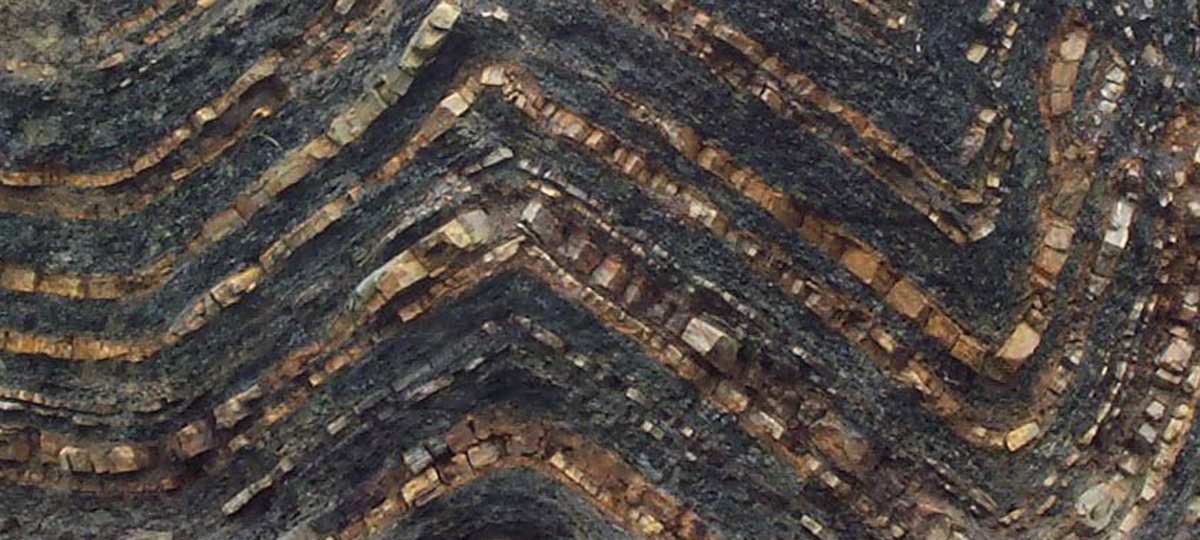
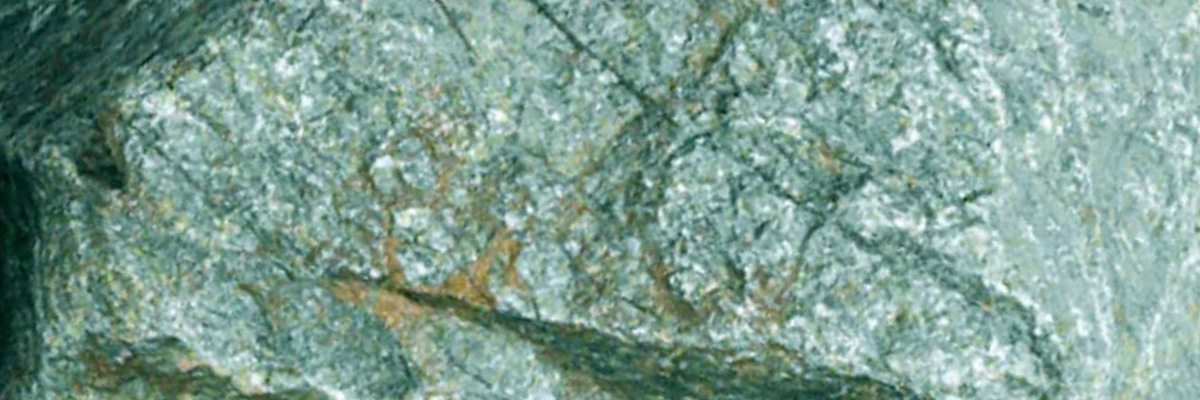
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks are a fascinating subgroup of metamorphic rocks that lack the distinct layering or banding commonly seen in foliated rocks. Instead, these rocks exhibit a more homogeneous, granular texture. Non-foliated rocks are formed under various pressure and temperature conditions, often with the presence of chemically-active fluids. They provide critical insights into the processes that shape the Earth’s crust and the formation of economically important mineral deposits.
Formation
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks, known as parent rocks, are exposed to heat, pressure, and chemically-active fluids during metamorphism. Unlike foliated rocks, the minerals in non-foliated rocks do not align themselves parallel to the applied pressure. This difference can arise from a combination of factors, such as the presence of minerals that do not easily form platy or elongated crystals, or the influence of chemically-active fluids on the rock’s mineralogy.
Types
There are several types of non-foliated metamorphic rocks, which are classified based on their parent rock, degree of metamorphism, and mineral composition. Some examples include:
- Hornfels:
A fine-grained, hard, and dense metamorphic rock that forms from the contact metamorphism of various parent rocks, such as shale, sandstone, or limestone. Hornfels are commonly found near intrusive igneous bodies, where they have been subjected to high temperatures. - Marble:
A coarse-grained metamorphic rock composed primarily of recrystallized calcite or dolomite, derived from the metamorphism of limestone or dolostone. Marble is often used as a building and decorative stone due to its beauty and resistance to weathering. - Quartzite:
A hard, non-foliated metamorphic rock composed almost entirely of recrystallized quartz, formed from the metamorphism of sandstone. Quartzite is highly resistant to weathering and erosion and is often used in construction and as a decorative stone. - Greenstone:
A non-foliated metamorphic rock composed mainly of green minerals, such as chlorite, epidote, and actinolite. Greenstones are typically derived from the metamorphism of basaltic or other mafic rocks and are often associated with ancient volcanic arcs.
Properties
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks exhibit a range of properties that reflect their diverse origins and compositions. They can range from fine-grained to coarse-grained and have a granular, crystalline, or dense texture. Due to their lack of mineral alignment, non-foliated rocks tend to be isotropic, meaning their properties are uniform in all directions. They are generally more resistant to weathering and erosion than their foliated counterparts.
Significance
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks have significant importance in various fields. In geology, they provide valuable insights into the range of pressure, temperature, and fluid conditions that can influence metamorphism and help us understand the formation of economically important mineral deposits.
Non-foliated rocks also have important commercial and industrial uses. Marble is widely used in architecture and sculpture due to its aesthetic appeal and durability. Quartzite is used in construction, road building, and as a decorative stone for its strength and resistance to weathering.
By studying non-foliated metamorphic rocks, scientists can better understand the diverse processes shaping our planet and the factors that influence metamorphism. These homogeneous wonders reveal the intricate connections between Earth’s tectonic forces, temperature, and chemistry, helping to expand our knowledge of the dynamic world beneath our feet.
Examples
-
Anthracite
Anthracite is a type of metamorphic rock that belongs to the coal family, ranking as the highest-grade coal due to its high carbon content and …
-
Granulite
Granulite is a high-grade metamorphic rock, belonging to the granulite facies, that forms under extreme heat and pressure within the Earth’s crust. This rock exhibits …
-
Greenstone
Greenstone is a metamorphic rock that belongs to the greenschist facies, a sub-class of low-grade metamorphic rocks. It is characterized by its greenish hue, which …
-
Hornfels
Hornfels is a non-foliated metamorphic rock characterized by its fine-grained, dense, and hard texture. This rock type forms under high-pressure and moderate-temperature conditions during the …
-
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock that belongs to the non-foliated class, meaning it lacks a layered or banded appearance. Formed from the metamorphism of limestone …
-
Quartzite
Quartzite is a non-foliated metamorphic rock that originates from the metamorphism of pure quartz sandstone. Known for its remarkable hardness and durability, quartzite typically displays …
Related Posts
-

Metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks are a fascinating class of rocks that have undergone transformation due to intense heat, pressure, or mineral exchange deep within the Earth’s crust. …
-

Organic Sedimentary
Organic sedimentary rocks are unique formations derived from the accumulation and preservation of plant and animal remains, providing a window into Earth’s biological history. These …
-

Chemical Sedimentary
Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed from the precipitation of dissolved minerals from water, often due to changing environmental conditions. These captivating rocks offer valuable insights …